where is glucose 6 phosphate found Glucose phosphate metabolism glycogen enzyme glycolysis fate phosphorylase central epomedicine into formation converts
Glucose: A Life-Saving Compound When it comes to our body’s energy source and one of the most critical molecules in our lives, glucose goes beyond just a sweet treat. It’s a life-saving compound that our bodies rely on to fuel the cells that keep us moving. Glucose 6-phosphate and glucose 1-phosphate are two important derivatives of glucose that play key roles in our metabolism. Glucose 6-phosphate, which is formed by the reaction between glucose and ATP, is central to glucose metabolism. This molecule is critical in glycolysis, the first step in the breakdown of glucose for energy. Additionally, glucose 6-phosphate is important in the synthesis of glycogen, the storage form of glucose in our bodies. Our liver and muscle cells use glucose 6-phosphate to create glycogen for energy storage, ensuring that we always have an accessible source of energy when needed. Similarly, glucose 1-phosphate plays a key role in energy metabolism too. It is formed through the action of the enzyme phosphoglucomutase on glucose 6-phosphate and is used in the synthesis of UDP-glucose and glycogen. As the starting material for glycogen synthesis, glucose 1-phosphate is essential for our energy storage capabilities. It’s apparent that glucose and its derivatives are crucial for energy metabolism, but our bodies are continuously regulating glucose levels to keep them in check. Too much or too little glucose in the blood can have negative consequences. When our glucose levels rise, our bodies release insulin to help transport glucose to our cells for energy use or storage. On the other hand, when glucose levels fall, our bodies release glucagon to mobilize stored glucose (glycogen) to be broken down into glucose for energy use. However, it’s important to note that an excess of glucose in our bodies can lead to health problems. Diabetes, a chronic medical condition, is characterized by high levels of glucose in the blood. For those with diabetes, the regulation of glucose levels in the body is impaired, leading to long-term complications. Healthy glucose levels are vital to maintain good health. In conclusion, glucose and its derivatives such as glucose 6-phosphate and glucose 1-phosphate are vital to our energy metabolism and overall health and wellbeing. The regulation of glucose levels in our bodies is essential to ensuring our cells have enough energy to perform their functions effectively, but maintaining healthy glucose levels takes effort. Eating a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise can help keep your blood glucose levels in check, and ensure your body has an ample supply of glucose to function efficiently.
If you are looking for Glucose 1- Phosphate | SIELC you’ve came to the right place. We have 5 Images about Glucose 1- Phosphate | SIELC like Glucose-to-Glucose-6-Phosphate - PhD Muscle, Glucose 6 Phosphate : Central to Glucose Metabolism | Epomedicine and also Glucose-to-Glucose-6-Phosphate - PhD Muscle. Read more:
Glucose 1- Phosphate | SIELC
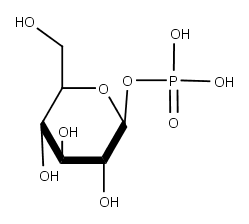 sielc.comglucose phosphate sielc
sielc.comglucose phosphate sielc
Glucose-6-phosphate - Encyclopedia Article - Citizendium
 en.citizendium.orgglucose phosphate citizendium
en.citizendium.orgglucose phosphate citizendium
Solved: Glucose-6-phosphate Dehydrogenase Is Also Found In… | Chegg.com
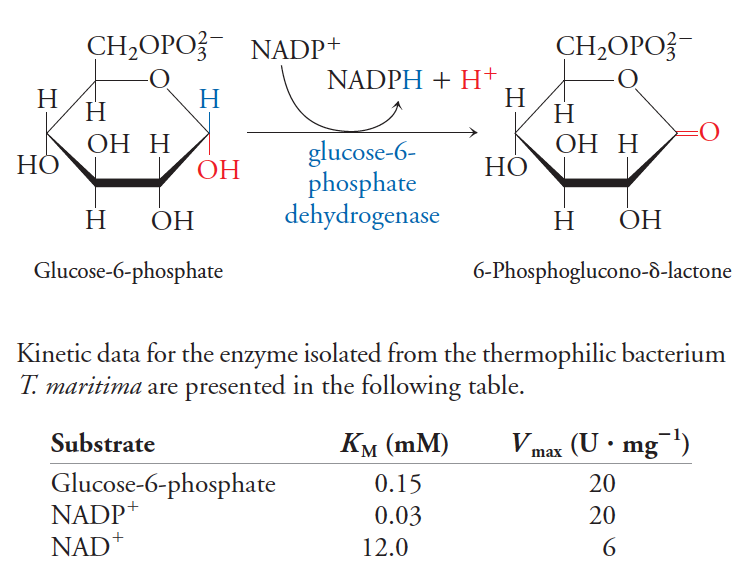 www.chegg.comglucose phosphate dehydrogenase reaction solved ki inhibitor problem inhibited
www.chegg.comglucose phosphate dehydrogenase reaction solved ki inhibitor problem inhibited
Glucose-to-Glucose-6-Phosphate - PhD Muscle
 phdmuscle.comglucose phosphate interactions
phdmuscle.comglucose phosphate interactions
Glucose 6 Phosphate : Central To Glucose Metabolism | Epomedicine
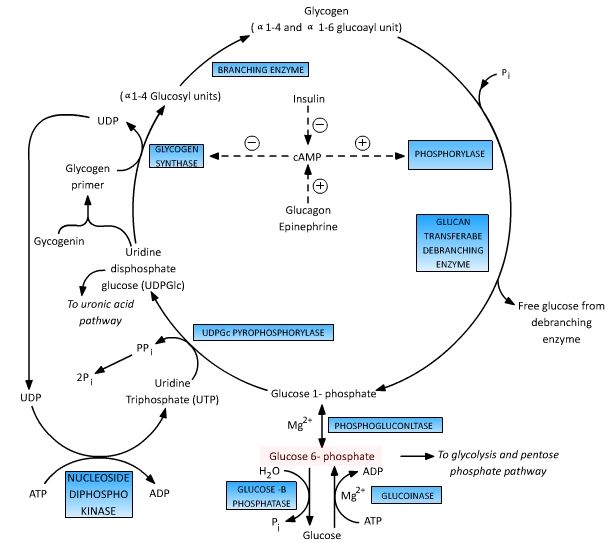 epomedicine.comglucose phosphate metabolism glycogen enzyme glycolysis fate phosphorylase central epomedicine into formation converts
epomedicine.comglucose phosphate metabolism glycogen enzyme glycolysis fate phosphorylase central epomedicine into formation converts
Glucose phosphate citizendium. Glucose phosphate interactions. Glucose 1- phosphate